Datatypes in Java-
In java every variable has a type, every expression has a type and all types are strictly defined. All the assignments should be checked by the compiler for the type compatibility. Hence java language considers as strongly typed language. Java is not considered as pure object oriented programming language because several OOP features(like multiple inheritance, operator overloading) are not supported by java. Even java contains non-object primitive datatypes .
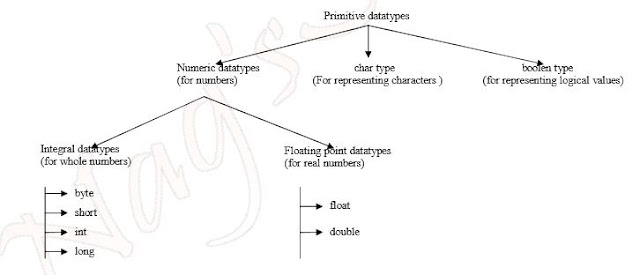
Except boolean and char all the remaining datatypes are signed datatypes i.e we can represent both +ve and –ve numbers.
byte ---
Size : 8-bits
Range: -128 to 127
-ve numbers can represented in 2’s compliment form.
Ex:
byte b = 10;
byte b = 127;
byte b = 130; C.E: possible loss of precision
byte b = true; C.E: Incompatible types found: boolean required: byte byte datatype is best suitable if we are handling data either from file or form network.
short ---
size = 2 bytes
range = -215 to 215 -1 (-32768 to 32767)
Ex: short s = 10;
short s = 32767;
short s = 65535; C.E: possible loss of precision.
short s = true; C.E: Incompatible types short is best suitable datatype for 16-bit process. But currently these are completely out dated and hence the corresponding datatypes also no one is using.
int ----
The most commonly used datatype is int.
size = 4 bytes
range = -231 to 231 – 1(-2147483648 to 2147483747)
The size of int is always fixed irrespective of platform hence the chance of failing java program is very less if u r changing the platform hence the java is considered as Robust.
long ---
if int is not enough to hold big values then we should go for long-
datatype
size = 8 bytes
range = -263 to 263 – 1
Ex: The amount of distance traveled by light in 1000days can be represented by long datatype only and int is not enough.
floating-point ---
for representing real numbers(numbers with decimal points)
floating –point datatypes divided into two types
float and double
Float--
size = 4 bytes
range = -3.4e38 to 3.4e38
If 6 to 7 decimal places of accuracy required
Considered as single precision
Double---
Size=8 bytes
range = -1.7e308 to 1.7e308
If 14 to 15 decimal places of accuracy required
Considered as double precision
boolean datatye
size = not applicable(virtual machine dependent).
range = not applicable but allowed values are true/false.
Which of the following boolean declarations are valid
boolean b1 = true; (Right)
boolean b2 = 0; (Wrong) Incompatible types found:int required : boolean boolean b3 = TRUE;(wrong)capital TRUE is not valid
Ex: int x = 0;
if(x) {
System.out.println("Hello"); }
else {
System.out.println("Hai"); }
C.E: Incompatible types found :int required: boolean.
char ----
java provides support for Unicode i.e it supports all world wide alphabets. Hence the size of char in java is 2 – bytes. And range is 0 to 65535.



